The uses and purposes of 3D printing
This chapter is intended for those who are interested in 3D printing in general and also for those who are interested in producing any part or product using 3D printing.
Preface
There is a wide variety of 3D printing technologies in the world. Each technology has unique uses, advantages and disadvantages. In order to choose the best technology for 3D printing, one must first define the user’s need and then select the printer with the most appropriate characteristics that will meet the needs and use of the product.
This chapter will present a variety of uses that can be made with 3D printing.
The 3D printer industry has been growing at a dizzying pace in recent years and with it come a large number of 3D printing technologies. How many 3D printers are there in the world ?
As of 2018, 135 companies worldwide have manufactured and sold industrial 3D printers. For example, the desktop company sold over 500,000 3D printers.
In 2017, 1,768 metal printers were sold compared to 983 printers in 2016 (an increase of almost 80 percent).
30% of the 300 largest brand companies in the world use 3D printing.
Source: Forbes
The different uses of 3D printing in various industries
You can ask what can be done with a 3D printer? In this section we will describe what can be printed using different printing technologies and how the different uses are reflected in the variety of industries.
3D printing in the medical field
In the last decade and in recent years in particular, we have learned about dozens of projects in the medical industry and medical devices that have been carried out in combination with 3D printing, especially in the service of surgery. In Israel there is development of advanced medical applications and the technology has even entered increased use within hospitals. 3D prints are used to create implants, models for practice and surgical learning.
Source: Verdict
3D printing in Engineering
3D printers are used by the engineering industry from the development stage to the production of final products. Rapid printing of models enables feasibility tests and proofs, and enables increased speed and efficiency in testing the structure and mechanics of products. This fact results in time savings compared to traditional processes. The engineering industry is already using printed products not only for prototypes, but also for mechanical products with mechanical reliability that are used as finished parts in active products.
The impact of 3D Printing on architecture
Modeling is an integral part of the architectural process. 3D printing enables fast model production, compared to a manual technique that consumes many manpower hours. 3D printing makes it possible to significantly reduce the manpower employed in models creation, and shortens the number of working days required to supply models to the designer or marketer. In addition, the technology enables the creation of extremely complex geometric shapes that are difficult to achieve with only the help of manual design. 3D printing technology is used by architects to model large neighborhoods, city-building planning models, and interior models, which allow for a reduction to small details and textures. The scale of the models can be easily changed on the computer and it is possible to produce many models at different scales quickly and efficiently.
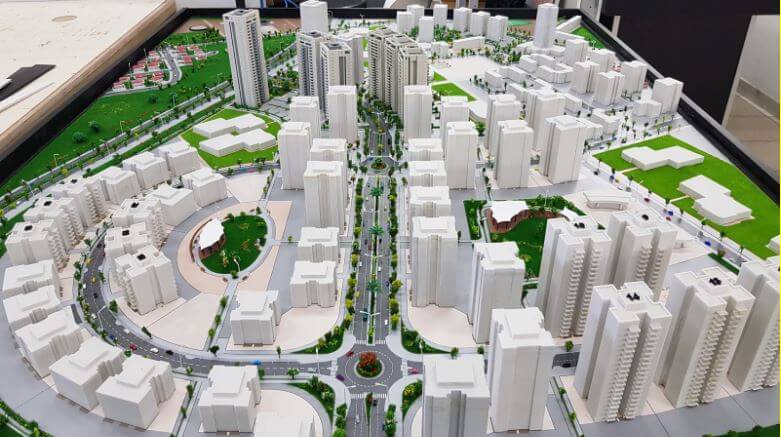
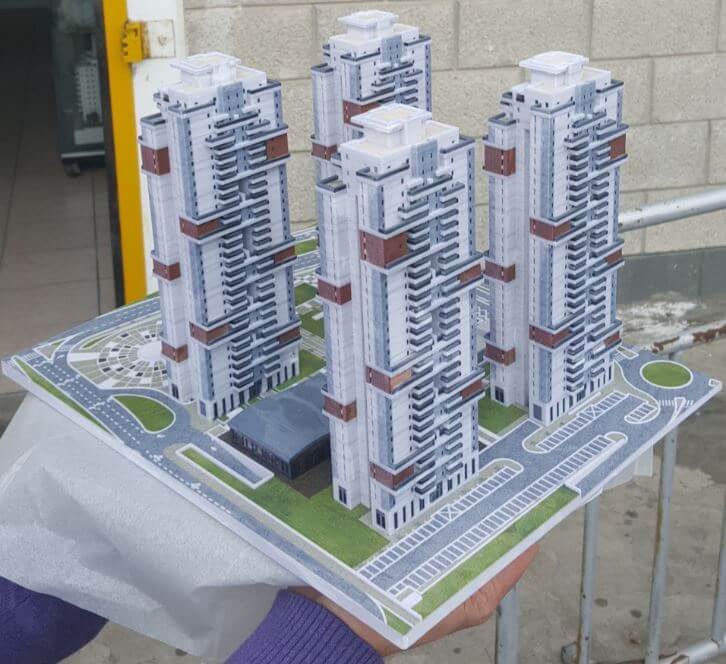


3D Printing in industrial design
In this industry, 3D printers allow designers to focus on developing design ideas and reduce the traditional preoccupation with continuous processing and product construction. The printers make it possible to produce geometries that could not be produced with the help of manual design. In addition, a computerized repository of re-printable designs can be produced. The 3D printing process allows designers to get quick physical, tangible and 3D feedback in no time from the moment the design idea was used. This technology enables freedom of action and new opportunities in the design world.
3D Printing in fashion design industry
Various 3D printing technologies open up a whole new world of fashion design possibilities. From the production of printed fabrics to the printing of metal buckles. With the help of three-dimensional printing, complete clothes consisting of designed segments can be produced. 3D printers enable the production of clothes with an innovative look that could not be achieved in the past. Another use for 3D printing in the fashion world is reflected in the printing of custom shoe soles. 3D printing allows elasticity and control over the structure of materials.
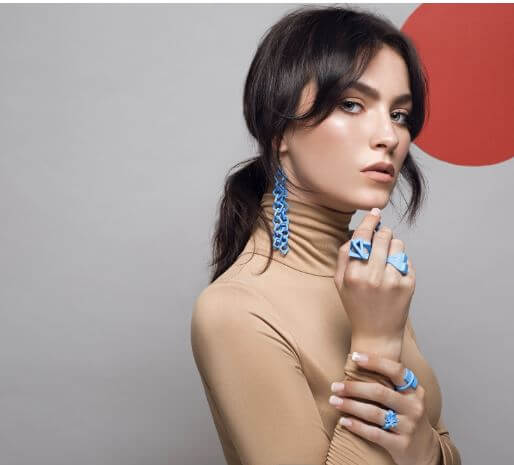
3D Printing technology for jewelry
3D printing allow for custom production of prototypes and finished jewelry. The use of 3D printers allows for individual adjustment of the jewelry and rapid change of the models based on the structure of previous models. Jewelry designers use 3D prints both to produce the final products with the help of various plastic materials or metals, and to produce printed molds to which the desired materials are poured. It is also possible to produce a “pupa” around which the mold to which the disappearing wax method is poured is produced. 3D printing technology enables the creation of diverse geometries that have not been possible in the past in any other technology, and therefore allows designers to create innovative looks that have never been seen before.

3D Printing in education
The constant development in the world of 3D printing today also affects the world of education, both in creating tools of instruction for teachers and as a professional tool for students developing their own products. This technology allows students to produce tangible models of their ideas and correct mistakes in models quickly at low cost. Unlike the production of models with the help of manual processes, students can return to the computer model and improve it even after the model is produced. As part of the development process, students can develop knowledge in the areas of mathematics, analysis, spatial vision and a wide range of other abilities.
For extended learning on ways to integrate 3D printing in the world of education
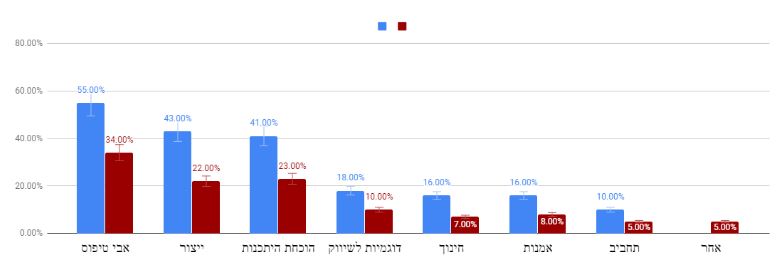
By years : 2017–2018
The graph shows statistics on the use of 3D printing in various industries around the world between the years 2017-2018.
The data were taken from the site: Statista
- Chapter 1
What is 3D printing and what are its origins? - Chapter 2
The uses and purposes of 3D printing - Chapter 3
3D Printing Process - Chapter 4
How to choose 3D printing technology - Chapter 5
Overview of various 3D printing technologies - Chapter 6
General design guidelines for 3D printing - Chapter 7
CAD software classification - Chapter 8
3D Printing STL files: Introduction - Chapter 9
Understand common STL files errors and how to fix them - Chapter 10
SLS to MJF comparison - Chapter 11
Metal 3D Printing: Introduction - Chapter 12
How 3d metal printing change the world - Chapter 13
Metal 3D Printing Pros & Cons
- Chapter 1
What is 3D printing and what are its origins? - Chapter 2
The uses and purposes of 3D printing - Chapter 3
3D Printing Process - Chapter 4
How to choose 3D printing technology - Chapter 5
Overview of various 3D printing technologies - Chapter 6
General design guidelines for 3D printing - Chapter 7
CAD software classification - Chapter 8
3D Printing STL files: Introduction - Chapter 9
Understand common STL files errors and how to fix them - Chapter 10
SLS to MJF comparison - Chapter 11
Metal 3D Printing: Introduction - Chapter 12
How 3d metal printing change the world - Chapter 13
Metal 3D Printing Pros & Cons